SEO opportunities are limitless – so are the SEO technicalities. One of them is SEO redirects. In theory, URL redirecting means pointing the website visitors to a specific URL.
However, URL redirection from the SEO standpoint is a different ball game. There may not be any major differences in the redirection process, but the purpose and implications might vary.

If you’re figuring out URL redirects or SEO redirects, then you’re in safe hands as this will guide you on all the important aspects related to redirects in a simple way, so that even a fifth grader can understand this concept.
What’s a redirect?
A redirect swiftly guides website visitors to a different URL. The action of taking the website visitor from one URL to another URL is called the URL redirection process.
The goal of a URL redirection is to instantly drive the visitor landed on the page to a different destination page or website.
Beyond mere redirection, its SEO implications vary, making it essential to delve deeper into this aspect.
When to use redirects?
- Changing domain name: Changing domain names for branding or SEO strategies necessitates redirecting the old domain to the new one.
- Deleting outdated content: Deleting obsolete content requires redirecting the URLs to the most relevant, up-to-date posts.
- Merging acquired websites: Merging acquired websites is a strategy to enhance search engine visibility; redirects play a crucial role in this process.
- Fixing broken links: To resolve broken links pointing to non-existent pages, URL redirection proves invaluable.
- Avoiding 404 errors: Preventing 404 errors involves temporary redirects to informative pages during maintenance or changes.
SEO redirects Vs. URL redirects

In essence, an SEO redirect is a specific type of URL redirect implemented with the primary objective of optimizing search engine visibility and preserving SEO value during website changes. URL redirect, as a broader term, encompasses a range of redirection scenarios that may or may not primary focus on SEO.
SEO redirect:
An SEO redirect refers to the process of redirecting a URL with the specific goal of optimizing the website’s search engine performance. The primary objective is to enhance the site’s SEO standing by ensuring that search engines understand the changes in URLs and can appropriately index the content.
Key Aspects:
- Permanent move: SEO redirects often involve permanent redirections, commonly implemented using a 301 redirect. This signals to search engines that the move is permanent, and they should transfer the ranking value (link equity) to the new URL.
- Preserving SEO value: The focus is on preserving the SEO value of the old URL, such as backlinks and authority, and transferring it to the new URL. This ensures a smooth transition without losing search engine visibility.
- Relevant content mapping: SEO redirects are strategically used to guide users and search engines to the most relevant content, aligning with best practices for user experience and SEO.
Related: How to Create an SEO Friendly URL: Ultimate Tips
URL redirect:
URL redirect, on the other hand, is a broader term that encompasses any situation where one URL points to another. While SEO considerations are vital, URL redirects can be implemented for various reasons beyond SEO, such as website restructuring, branding changes, or fixing broken links.
Key Aspects:
- General redirection: URL redirects include any redirection of a URL to another, irrespective of the intent. It could be temporary (302) or permanent (301) based on the specific needs.
- Diverse use cases: URL redirects are not solely tied to SEO. They can be employed for various purposes, including rebranding, restructuring websites, managing broken links, or simply creating a better user experience.
- Temporary changes: While some URL redirects may be permanent for SEO reasons, others might be temporary, indicating a temporary move or a page that will revert to its original state.
Why are redirects important?

Understanding why redirects matter in SEO is fundamental before implementing them.
To help readers understand better, let us share some key aspects of URL redirection that will help understand why redirects matter so much in SEO:
1. Enhance user experience through smooth navigation:
One of the common use cases of URL redirection is navigating the website visitors toward a new or better destination page. SEO redirects ensure a seamless user experience, as often deleted web pages are redirected to the closest and relavant page.
Improving user experience is paramount; redirects ensure visitors land on the most suitable pages, adding value and improving overall satisfaction.
2. Aid the rebranding efforts:
During rebranding, where companies change names, logos, or domains, URL redirects assist in smoothly transitioning users to the new identity.
URL redirection does help in rebranding, especially when a company changes its name and domain. They have to redirect the website visitors to the new domain, and that’s where they use URL redirection.
3. Communicate with Search Engines:
One of the reasons why a URL redirect is important for SEO is that it communicates with search engines and lets the search engines know about the status of the URL.
There are different types of URL redirects used by the website owners, such as 301, 401, 404, and others, conveying the intent of website owners and influencing the SEO standing.
4. Manage outbound links:
When a blog or website adds a link to another website or blog, they’re creating an outbound link.
A proper URL redirection strategy in place is crucial to your website’s SEO, especially when you link to external sources.
Are URL shorteners good for URL redirection?
Using URL shorteners for redirection is beneficial for several reasons. Firstly, they create concise and user-friendly links, enhancing the overall user experience. Shortened URLs are visually appealing and easy to share across various platforms, making them ideal for marketing and social media campaigns.
With features like branded domains and detailed analytics, Replug ensures that your redirection strategy is not only efficient but also optimized for better results. Overall, URL shorteners simplify the redirection process, making it more accessible and impactful for both content creators and users.
Shorten your links, amplify your brand.
Create shareable, trackable and fully customizable branded urls. Get more clicks with absolute link management features such as Bio Links, retargeting, deep Links, CTA’s and more.
Learn More!
Types of redirects
| Sr. | Redirect Type | Purpose | Implementation | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | 301 redirect | Used for permanent URL changes. | Instructs search engines that the original URL has permanently moved to a new location. | Passes the majority of the original page’s ranking power to the new URL. |
| 2. | 302 redirect | Indicates a temporary move of a URL. | Instructs search engines that the move is temporary, and the original URL might be used again in the future. | Does not transfer as much ranking power as a 301 redirect; it’s more suitable for short-term changes. |
| 3. | 303 redirect | Temporary redirect similar to a 302, but with a different HTTP response code. | Less commonly used in digital marketing and SEO. | Does not play a major role in SEO strategies. |
| 4. | 307 redirect | Similar to a 302 redirect, indicating a temporary move. | Maintains the original HTTP method when redirecting the visitor. | Retains less ranking power than a 301 redirect but more than a 302 redirect. |
| 5. | 308 redirect | Indicates a permanent move similar to a 301 redirect. | Retains the original HTTP method when redirecting the visitor. | Similar to a 301 redirect but less commonly used in practice. |
| 6. | Canonical Redirect | Resolves duplicate content issues by specifying the preferred version of a page. | Involves adding a canonical tag to the HTML head section | Helps consolidate link equity and avoids content duplication issues. |
| 7. | HSTS Redirect | Enforces secure connections by redirecting HTTP requests to HTTPS. | Configured on the server using HSTS headers. | Boosts site security and can positively impact SEO. |
| 8. | A/B Testing Redirects | Tests variations of a page by redirecting a portion of users temporarily. | Involves using 301 and 302 redirects for different groups of users. | Should be used cautiously to avoid negative effects on search rankings. |
| 9. | Meta Refresh Redirect: | Redirects after a specified amount of time (often used for immediate redirects). | Achieved through a meta tag in the HTML head section. | Less favored for SEO as it may not pass ranking power as effectively as server-side redirects. |
| 10. | Redirect Using a URL Shortener | Creating efficient, shareable branded links with added tracking capabilities. | Select a reputable URL shortening service like Replug to minimize potential risks. | URL shorteners typically employ 301 redirects for minimal SEO impact. |
SEO redirects: Best practices of URL redirection

The primary goal in SEO of URL redirection is to gain the SEO benefit from the previous domain and make it easier for the visitors to click through and discover the page or content.
Follow these 7 best practices for effective URL redirection:
1. Establish a URL redirection strategy
Developing a crystal clear redirection strategy helps create a URL redirection road for the SEO team to follow.
It’s good to keep everything related to SEO and redirection documented so that the team members can stay up-to-date with the strategy.
2. Prefer server-side redirects
Most SEOs prefer server-side redirects like 301 and 302 are preferred as they’re easier, faster, and more reliable to implement as compared to client-side redirects.
The client-side redirects are Javascript-based, which might not be easy to implement for beginners.
3. Avoid redirect chains
Redirect chain is a URL redirection practice that redirects from one URL to another and then to another. It’s best to avoid redirect chains because it can easily confuse website visitors and search engines.
Plus, one of the reasons why you should avoid redirect chains is that it can increase page loading speed.
4. Keep the internal links updated
Navigation is an important aspect of website optimization that directly impacts the user experience and search engine bots’ crawling.
When a redirect is implemented, it’s necessary to update the sitemaps so that search engine bots can navigate to all pages. Similarly, internal links shouldn’t be broken to avoid disruption in the user experience.
5. Monitor redirects regularly
Redirection is one of the link management strategies used by digital marketers and SEO to drive website visitors and search engine bots to specific links or pages.
It’s vital to closely monitor and analyze the redirects from time to time to ensure they’re working just fine.
6. Redirect to the most relevant content
Make sure that you’re redirecting your pages to the closest match content on the website.
It’ll increase engagement, entice the reader to continue reading the content and impact the overall user experience of the page. So, don’t shy away from finding the most relevant content for redirecting.
7. Redirect HTTP to HTTPS
First things first, HTTPS is recommended for every website as it improves your site’s reputation among users and search engines. While some believe it’s a small ranking factor.
Most website hosting companies automatically add an HTTP to HTTPS redirection when an add-on domain is added to the hosting account. However, if this redirect isn’t working for you then you should contact your web host.
Related: What Does HTTP 302 Code Means For URL Shorteners?
John Mueller’s tips on redirects
John Mueller advises focusing on using the technically correct redirect type and not being overly concerned about its impact on PageRank.
Here’s another tip on how long a site should keep a redirect after a site move and what type of redirects are best in such situation.
Furthermore, John Mueller discusses how a Googlebot interacts with HSTS /307s
Here he discusses best ways to deal with those 404 errors.
Are URL shorteners safe to use?
Using URL shorteners can be safe, but it’s essential to choose a reputable service. Trusted URL shorteners, employ security measures to ensure the safety of users and their data. They generate shortened links that redirect users to the intended destination without compromising security.
However, caution should be exercised when using unknown or unreliable URL shorteners, as malicious actors may exploit them to mask harmful links. Always opt for established services that prioritize user security and provide features like link tracking, analytics, and customization.
Related: How to Redirect a URL using Replug?
10 Methods to implement a redirect
Choose the method that aligns with your technical skills, website platform, and specific redirect requirements. Always consider SEO implications when implementing redirects to ensure a positive impact on search rankings.
1. .htaccess file (Server-side redirect):
- Method: Edit the .htaccess file on your web server.
- Example (301 Redirect):
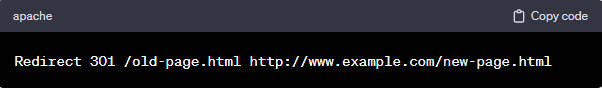
- Use Case: Suitable for Apache servers. It’s a powerful method for server-side redirects.
2. Server-side scripting (PHP, Python, etc.):
- Method: Use server-side scripting languages to implement redirects.
- Example (PHP – 301 Redirect):
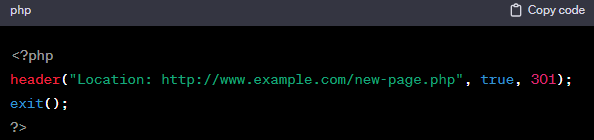
- Use Case: Useful if you have dynamic content or want to handle redirects programmatically.
3. WordPress plugins (CMS-specific):
- Method: Utilize plugins if your website is built on a content management system (CMS) like WordPress.
- Example (Link Whisper Plugin):
- Use the plugin’s redirect settings to specify source and target URLs.
- Use Case: Ideal for non-technical users managing their websites on platforms like WordPress.
4. Meta refresh (HTML redirect):
- Method: Use the
<meta>tag to trigger a redirect after a specified time. - Example (Immediate Redirect):
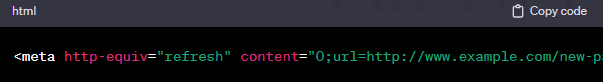
- Use Case: Simple but may not be the best for SEO; suitable for immediate redirects.
5. Javascript redirect:
- Method: Implement a redirect using JavaScript code.
- Example:
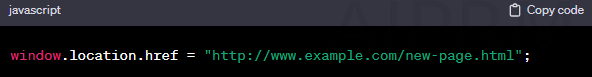
- Use Case: Can be useful, but search engines may not always interpret JavaScript redirects effectively.
6. CMS-specific redirection modules:
- Method: Some CMS platforms have built-in redirection modules.
- Example (Drupal):
- Use Drupal’s “Path Redirect” module to manage URL redirects.
- Use Case: Streamlines the process for users familiar with the CMS.
7. Cloud-based redirection services:
- Method: Use online services that provide redirection features.
- Example (Replug):
- Utilize an all-in-one URL shortener and link management tool for redirects.
- Use Case: Suitable for users who prefer a web-based interface and additional link management features.
8. Web server configuration:
- Method: Adjust server configuration files to handle redirects.
- Example (Nginx – 301 Redirect):
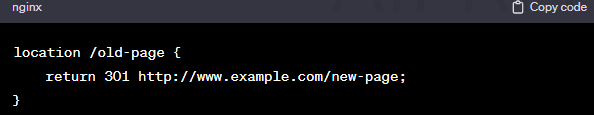
- Use Case: Useful for server administrators with access to server configurations.
9. Content Delivery Network (CDN) configuration:
- Method: Leverage CDN settings for URL redirects.
- Example (Cloudflare):
- Use page rules to set up redirects.
- Use Case: Can be convenient for users who utilize CDNs for performance and security.
10. Dynamic Redirects using Programming Frameworks:
- Method: Use web frameworks for dynamic redirects.
- Example (Django – Python):
- Implement a dynamic redirect based on certain conditions.
- Use Case: Suitable for applications with complex redirect logic.
Redirection checker tools
Here’s a list of some popular Redirection Checker Tools:
- Screaming Frog:
- Description: Advanced SEO analysis tool with redirection-checking capabilities.
- Website: Screaming Frog
- Ahrefs:
- Description: Comprehensive SEO analysis tool including redirection analysis.
- Website: Ahrefs
- Semrush:
- Description: All-in-one SEO toolkit with redirection analysis features.
- Website: Semrush
- Redirect Checker:
- Description: Simple, free tool to analyze redirects and status codes.
- Website: Redirect Checker
- Whatsmydns Redirect Checker:
- Description: Online tool for checking website and domain DNS settings, including redirects.
FAQs about URL redirection
Let us answer some of the commonly asked questions about URL redirection:
Can you apply a redirect in a URL?
You can apply a redirect to any URL you own or manage. However, the URL redirect application happens either in the .htaccess file or using a redirection script or SEO WordPress plugin.
Can I redirect a URL for free?
Absolutely. You can set up a URL redirection for free as long as you manage/control the current URL and own the new destination URL you’re redirecting the URL to as a result of this process.
How do I redirect a URL in Chrome?
The URL redirection needs to be set up on the code level. It doesn’t matter what browser the end user is using for website surfing. The URL redirection would occur if it’s done right.
How does a URL redirect work?
The URL redirection works using a piece of code inserted either into the .htaccess file or using a script or a WordPress plugin that takes the end user to the new destination URL defined using the redirection setup.
How do I redirect a URL for free?
You can simply opt for a redirection WordPress plugin like Redirection to create redirects on your WordPress website for free.
What is an example of URL redirection?
The answer is quite simple: just type in fb.com in your browser’s address bar and press enter. You’ll be redirected to the facebook.com. Facebook owns fb.com and redirects this short URL to its main URL.