What is URL Hijacking?
URL hijacking is when hackers redirect users to fake websites to trick them into sharing sensitive information. Once you land on the bogus site, you might be asked to provide your login credentials, financial information, or other sensitive data. This could lead to identity theft, financial losses, and other severe consequences.
It’s no surprise that digital marketers, bloggers, and website owners face a wide array of challenges, especially when their sites or brands start to take off on social media or search engines.
Most of us already know about hacking attempts on websites. However, most people don’t know about URL hijacking and how to prevent your website from it.
Since URLs are an essential part of online marketing, social media management, email marketing, and paid advertising, it’s vital to stay vigilant about the vulnerabilities attached to URLs.
We’ll try to go deep down into this topic and educate you on URL hijacking, its impact on brand positioning, and how to avoid it.
URL hijacking is a malicious technique utilized by cybercriminals to redirect users to fraudulent websites, where they might be prompted to disclose sensitive information. It is a cybersecurity threat where attackers manipulate website URLs to redirect users to a fake website that looks almost identical to the original one. The fake website aims to deceive users into providing sensitive information such as login credentials, personal details, or financial information. Therefore, it is imperative to exercise vigilance and implement protective measures such as verifying URLs, employing anti-phishing software, and maintaining updated security protocols on all devices.
Types of URL Hijacking
1. Paid search hijacking
Paid search hijacking is a type of hijacking that involves putting an identical copy of a company’s ad in the paid search results, targeting the same target audience and reaching out to them by outbidding the ad of the actual brand with a few cents.
Mostly affiliate marketers who don’t abide by the rules and terms of the affiliate programs/networks are involved in playing such tricks on companies.
2. Browser hijacking
 Browser hijacking is an activity of installing unwanted softwares to the web browser without the user’s consent for various reasons, such as spying on users, stealing their sensitive information, or bombarding them with adverts.
Browser hijacking is an activity of installing unwanted softwares to the web browser without the user’s consent for various reasons, such as spying on users, stealing their sensitive information, or bombarding them with adverts.
We all have had experiences, especially in the past, when clicking a link on a website opens a dozen more websites. Though most website builders use such strategies to gain more clicks and impressions on their display ads, it’s still a frowned-up tactic in the website-building community.
3. Typo-squatting
URL hijacking has a wide spectrum in the search engine marketing world, meaning it has different shapes and forms. Typo-squatting is a form of URL hijacking in which a person or company uses a misspelled version of the domain name to steal website visitors from the original website.
For instance, if a person tries to steal the traffic/users of netflix.com by registering a domain like neftlix.com, then it’s called typo-squatting – it’s just an example.
Anyway, some hackers or stinky website builders play such tricks on their competitors or top-notch companies by registering similar domain names and building websites to impersonate real brands or websites.
Related: How to Block a URL in Chrome?
What are hijacked domains used for?
It’s crystal clear that URL or domain hijacking has different levels, shapes and forms. I’ll shed some light on different patterns to look out for when identifying URL hijacking.
However, it’s important to learn why hackers hijack domains or URLs. When you know the evil purpose behind domain hijacking, you’ll be well-equipped to stop them and protect your online properties better.
Here are several reasons why domains are hijacked:
1. Stealing traffic
Website security is a serious concern for bloggers, website owners, and digital marketers. Hijacked domains can be used to steal traffic from legitimate websites. Attackers can create a website with a similar name to a legitimate website and use the hijacked domain to redirect traffic to their fake site.
This can result in legitimate traffic being redirected to the attacker’s site, potentially leading to financial loss for the legitimate site owner.
Related: Boost Your Website Traffic Through Social Media
2. SEO spam
SEO spam is a process in which an SEO desperately or intentionally tries to create backlinks to a website through blog commenting, link insertion, cold reach out, or other ways. The purpose of SEO spam is to generate backlinks so that they could benefit their website. However, it’s a negative SEO practice that is illegal and unethical.
In some cases, hijacked domains are used for SEO spam, which involves creating websites that are designed to manipulate search engine rankings. Some experts try to manipulate the SERP using their websites or hijacked domains.
The way it works is that they create multiple low-quality websites that link back to their main site, in an attempt to improve their website’s search engine ranking.
Related: How to Create an SEO Friendly URL: Ultimate Tips
3. Phishing attacks
 Phishing is a type of cyberattack in which an attacker sends fraudulent communications (usually via email or social media DM) that appear to come from a legitimate source in order to trick the recipient into disclosing sensitive information or taking a certain action.
Phishing is a type of cyberattack in which an attacker sends fraudulent communications (usually via email or social media DM) that appear to come from a legitimate source in order to trick the recipient into disclosing sensitive information or taking a certain action.
Hijacked domains can be used in phishing attacks as attackers can create URLs/links of legitimate websites to trick users into submitting their sensitive information or login credentials.
4. Email spam campaigns

Email marketing is an excellent digital marketing strategy. Brands and experts build email lists so that they don’t always rely on third-party platforms to interact with their followers. Hijacked domains can also be used in spam campaigns to distribute unsolicited emails.
Domain hijackers can use a hijacked domain to send spam emails that appear to come from a legitimate source, increasing the likelihood that the recipient will open the email and click on any links contained within it.
5. C2 Servers
Since there are various uses of hijacked domains, it’s hard to pin them down to just a few uses. Sometimes, hijackers steal domains to use for command and control (C2) servers for botnets or other types of malware. By using a hijacked domain as a C2 server, attackers can maintain control over infected devices and issue commands to them without being detected.
6. Malware distribution
 Attackers could have different reasons for spreading the virus and malicious files, for instance, stealing passwords or credit card info, or code insertion. The problem is that they could use hijacked domains to distribute malware to the users.
Attackers could have different reasons for spreading the virus and malicious files, for instance, stealing passwords or credit card info, or code insertion. The problem is that they could use hijacked domains to distribute malware to the users.
Attackers can create websites that appear legitimate or spread the links via email or social media and the users who click on those links may end up compromising their online security.
Related: Easy Guide For Fixing URL Blacklist
7. Fake news websites
One of the use cases of hijacked domains is spreading fake news on the web. It’s easier to distribute disinformation and propaganda content through hijacked domains because it’s hard to track the original source. Often the domain hijacking victims have no idea how and where their certain pages or URLs are being misused for spreading fake information or data.
How to recognize URL hijacking?
If someone is new to digital marketing, they may have a hard time figuring out signs of URL hijacking. To make it easier for everyone to recognize URL hijacking, here are some common ways to recognize URL hijacking:
1. The URL looks strange:
If the URL looks different from what you would expect, it may have been hijacked. Look for misspellings, added characters, or unexpected domains in the URL.
2. The website looks different:
If you visit the URL and the website looks different from what you would expect, it may have been hijacked. Look for changes in the website’s layout, content, or functionality.
3. You are redirected to another website:
If you click on the URL and are redirected to a different website, it may have been hijacked. Check the URL of the website you are redirected to and see if it matches the original URL.
4. Your browser warns you:
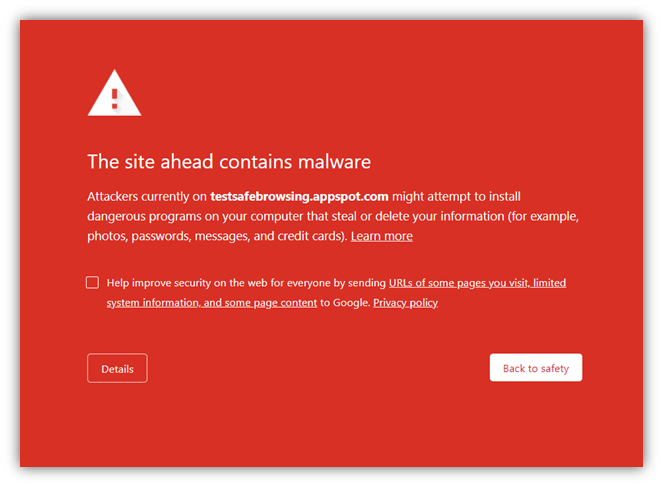 Some browsers will warn you if they detect that a website may be unsafe or has been hijacked. If your browser displays a warning message, take it seriously and avoid visiting the website.
Some browsers will warn you if they detect that a website may be unsafe or has been hijacked. If your browser displays a warning message, take it seriously and avoid visiting the website.
Why does URL hijacking occur?
It’s hard to pinpoint the cause of the URL hijacking to something specific because the reason may vary from case to case.
However, URL hijacking is a negative activity that doesn’t bring any good to the victim. Instead, it often damages the brand’s reputation, SEO growth, and website traffic.
Therefore, protective measures are imperative for online businesses, especially if you got competition in SEO.
No doubt that there is always an agenda behind URL hijacking, and the more you know about it, the easier it gets to figure out the problem, just in case.
Here are six of the common reasons why URL hijacking occurs:
- To gain unauthorized access to a user’s device
- To steal sensitive information, such as login credentials or personal data
- To spread malware or ransomware
- To redirect users to a malicious website that looks legitimate
- To carry out further attacks or gain financial gain
- To exploit vulnerabilities in a website’s security
You may also like: Build Custom Audiences Through URL Tracking
How to prevent domain hijacking?
Here are several ways to avoid domain hijacking:
1. Trademark your domain:
Trademarking your domain helps establish legal ownership of your domain or brand which protects against infringement or domain hijacking. So don’t sleep on this preventive measure for the safety of your brand.
2. Monitor for impersonation sites:
Regularly monitor websites that may be impersonating your domain or brand, and take immediate action if you come across any. No one should be stealing your website traffic, brand value, and ROI.
3. Register other versions of your domain:
Registering different country top-level domain names can prevent others from registering them and using them for malicious purposes. You don’t necessarily need a separate website for each domain. Instead, you could redirect the additional domains to your main URL.
Related: How to change a link name?
4. Utilize HTTPS:
An SSL certificate is a must these days. In fact, all major web browsers prompt safety messages to visitors who visit unsecured websites. Getting an SSL certificate for your website is an essential step in securing your website, as it encrypts data transmitted between the user and the server.
5. Educate your staff/customers:
Educate your staff and customers to be aware of phishing scams and other forms of cyber attacks, and train them on how to prevent them. You might be able to avoid some malicious attacks.
6. Report false websites immediately:
If you come across a website that is impersonating your domain, report it to the relevant authorities immediately. Also, you could track down their web hosts and provide them with all the details. They might also take appropriate action on such websites.
Related: Track Your Success: How to Create a Tracking Link?
7. Disavow canonical links:
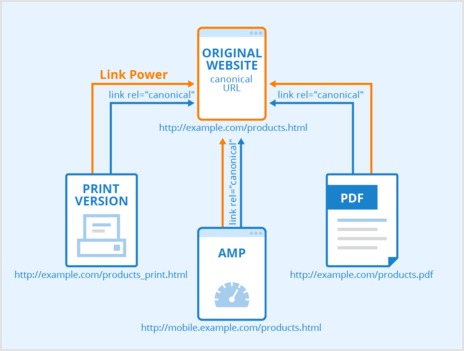
Disavowing canonical links means informing Google to ignore certain backlinks to your domain. It works as a proactive measure to be safe from search engine penalties. When search engines observe a disavowed canonical link, the chances are, it won’t be counted for or against you when ranking the specific pages in the SERP. It immensely helps against negative SEO.
8. Use URL hijacking removal tools:
Utilize software tools that can detect and remove hijacked URLs, preventing hackers from redirecting users to malicious sites. Try SEMrush, LinkResearchTools, or SISTRIX for this purpose.
6 SEO implications of URL hijacking
1. Losing search engine ranking:
Often when a website’s domain is hijacked, it may start to showcase some malicious activities that are a major red flag in the search engines’ eyes. It could result in a search engine ranking loss.
2. The decline in direct and organic traffic:
One of the setbacks for the hijacked domain is the traffic loss for the original site. The fake/manipulative URL may attract some of the original website’s traffic, leading to a decline in direct and organic traffic to the original website.
3. Massively affects brand positioning:
URL hijacking can massively impact a brand’s positioning by redirecting users to a completely different website that might not have the same brand values. Plus, some lookalike websites could steal customers and damage the brand’s reputation afterward.
4. The drop occurs in backlinks:
Backlinks are an essential SEO element. The problem with URL hijacking is that it could take away some of the backlinks to a website. Backlinks that were pointing to the original website will now be pointing to the hijacked website, leading to a drop in backlinks for the original website.
5. Search engines could flag the hijacked site:
Hackers could try to remove the original site from the SERP by filing DMCA complaints against the original site or hijacking the original site and portraying it as damaging for the end users. If search engines detect that a website’s URL has been hijacked, they may flag the hijacked site as spam or malicious, leading to further SEO implications.
6. Social media users are less likely to mention the site:
Social media plays a vital role in spreading the word about a brand or offer. When something goes wrong regarding domain hijacking, social media users may be less likely to mention or share the hijacked site, leading to a decline in social media traffic and brand awareness on social media platforms.
What is the impact of URL hijacking on brands?
URL hijacking can have severe impacts on a brand’s growth, clientele, and reputation. It’s vital to keep an eye out for such activities. However, it’s also important to understand the implications that URL hijacking may cause to help create preventive measures.
Let’s take a look at some of the impacts of URL hijacking on brands:
1. Loss of revenue:
URL hijacking can lead to a loss of revenue, as cybercriminals redirect potential customers to fake websites, resulting in lost sales. In some cases, credit card info gets stolen as a result of a security breach. Eventually, it becomes difficult for customers to trust the same website, leading to a decrease in repeat business and referrals.
Related: Boost your Advertising ROI using Post Click Optimization
2. Reduced customer loyalty:
No doubt that URL hijacking gets more damaging when customers get upset over the problem it causes. The issue is that it can affect customers’ loyalty when customers may feel deceived no matter what negative experience they have had as a result of URL hijacking. This can result in a loss of trust, decreased customer satisfaction, and a decline in customer retention.
3. Shrinking brand value:
URL hijacking can diminish a brand’s value, as it can damage the brand’s reputation and result in negative publicity. It’s a nightmare for any brand because it gets difficult for the brand to attract new customers and retain existing ones, leading to a decline in market share.
4. Identity theft:
Identify theft refers to stealing personal information and impersonating someone else in person or online. URL hijacking could lead to several problems and identity theft is one of them. Since hackers can use fake websites to steal personal information such as names, addresses, and credit card details, it could lead to financial troubles for the victim. As a result, it could lead to long-term financial repercussions.
5. Data breach:
URL hijacking is also used to breach data on websites, apps, and emails. Cybercriminals can use victims’ website URLs or lookalike URLs to gain access to sensitive data such as customer information, trade secrets, and financial data. This can result in significant financial losses, legal liabilities, and reputational damage.
Last thoughts on URL hijacking
No wonder brands, digital marketers, and affiliate bloggers spend hundreds of thousands of dollars and countless hours of work into building authoritativeness, trustworthiness, and online reputation. And when people go through such a bad experience or identify a red flag regarding their website or brand’s growth, it makes them want to tear their eyes out.
The purpose of this article is to educate everyone operating websites, online brands, or blogs that URL hijacking is real and what needs to be done just in case.
The gist of this piece is that you can hire all the cybersecurity experts and website analysts you want to tighten up your website security – something could still go wrong under your nose.
The only way to protect your brand is to educate yourself on cybersecurity and take every preventive measure possible.
FAQs about URL hijacking
Where are 301 and 302 redirects used?
A 301 redirect is a permanent redirect that informs search engines and browsers that a page or URL has moved permanently to a new location. It is used when you want to redirect an old URL to a new URL permanently without affecting the SEO rankings.
A 302 redirect is a temporary redirect that informs search engines and browsers that a page or URL has moved temporarily to a new location. This redirect is used when a website is undergoing maintenance or when a page is temporarily unavailable for some reason. Unlike a 301 redirect, a 302 redirect does not transfer the SEO rankings to the new URL.
What is reverse domain hijacking?
Reverse domain hijacking refers to the attempt of a trademark owner to obtain a domain name (or a different TLD of the brand name) by making false or misleading claims of infringement, even though the domain name was registered before the trademark was established.
How to prevent potential HTTPS URL hijacking?
There are various types of domain security certificates that one can buy to protect the domain and website from potential hacking and malicious attempts.
To prevent potential HTTPS URL hijacking, you can use a Certificate Authority that issues SSL/TLS certificates for your domain name and configure your web server to use HTTPS for all connections. Additionally, you should monitor your domain name’s DNS settings and make sure that no unauthorized changes are made.
What is the difference between URL hijacking and URL phishing, spoofing, or typo-squatting?
URL hijacking is the act of taking control of a domain name to redirect traffic to another website, while URL phishing, spoofing, or typo-squatting are different types of attacks that use deceptive tactics to trick users into visiting a fraudulent website.
Are redirects harmful? What is the risk of URL redirection?
Unwanted redirects could be damaging to the website’s SEO growth. Hackers could redirect website visitors to a malicious website or to a website that is not relevant to their search query.
The risk of URL redirection also includes the loss of link equity and potential impact on website ranking, especially if the redirection is not done correctly or the redirect target is not trustworthy.
Unwanted redirects are one of the tools of the negative SEO arsenal, so watch out for that.
You May Also Like:
What Are Tracking Pixels & How Do They Work?
Campaign Tracking: Data-Driven Tools for Marketers
Retargeting Ad Examples That Convert & Drive Growth
Benefits Of A Link Rotator: Why & When To Use Rotating Links?